- Published 10 Feb 2023
- Last Modified 29 Aug 2023
- 12 min
A Complete Guide to Epoxy Resin
Join us for an in-depth look at epoxy resins, how they are used, the common types and popular application methods.

Reviewed by Stephen Bettles, Technical Support Engineer (January 2021)
Epoxy resin is a versatile and highly adhesive material widely used in the construction, woodworking, and manufacturing industries. Its exceptional bonding properties, resistance to chemicals and moisture, and ability to withstand moderate temperatures make it a go-to choice for various applications.
From providing a waterproof barrier to heat resistance and high strength, epoxy resin offers a range of benefits. However, proper handling and safety precautions are crucial due to the potential hazards associated with certain formulations.
In this guide, we explore the uses, advantages, and limitations of epoxy resin, providing insights to help you harness its full potential in your projects.
What is Epoxy Resin?
Epoxy resin, also known as polyepoxide, is a type of adhesive used in a variety of applications and industries.
It has a particularly high level of flexural strength and is suitable for both domestic and commercial purposes. Formed of two parts, it is commonly mixed in ratios of between 2:1 and 4:1 resin to hardener. It also has the advantage of a particularly long pot life or working time, with the fast variety giving around 15 minutes of working time before gelling and the regular/slow variety expected to give roughly 100 minutes.
The positive qualities of epoxy resins include toughness, strong adhesion, and chemical resistance. Epoxy resin is used in a range of industries including construction and manufacturing. Additional uses include the building of electronic components such as fibre optics and electrical circuit boards.
How to Use Epoxy Resin Safely
There is a variety of safety precautions that should be taken into account when using epoxy resin.
Firstly, you should wear gloves to protect your hands against exposure to the resin and hardener liquids. Nitrile gloves are recommended as they are quite unlikely to react upon contact with the skin or resin. Baby wipes may be used to remove resin that does come into contact with the skin. Any remaining resin can be removed with a mixture of soap and water. Exfoliant is a particularly effective option for removal.
A plastic apron should be worn, allowing any spilt resin to be easily removed. You are also advised to wear safety goggles to protect your eyes. If there is any contact with the eyes, you should flush repeatedly with water for a period of 15 minutes and avoid rubbing. Medical attention should be sought at the earliest opportunity.
Lastly, it’s important to ensure that there is sufficient ventilation whenever you are working with epoxy resin. This may be achieved by opening the windows or switching on the ceiling fan in your work area. Alternatively, a respirator may be worn if you are unable to achieve a good level of ventilation. Browse some of the PPE you may need when using epoxy resin below:
What are the Different Types of Epoxy Resin?
Epoxy resin will fall under two principal categories - glycidyl or non-glycidyl. Glycidyl resins come under the subcategories of glycidyl-ether, glycidyl-ester, and glycidyl-amine. The non-glycidyl variety will either be aliphatic or cyclo-aliphatic. Glycidyl-ether epoxies are the most commonly used, particularly those of the bisphenol and novolac variety.
Bisphenol Epoxy Resins
Bisphenol-A diglycidyl ether (DGEBA) is a commonly used variety of commercial epoxy resin. It is produced as a result of the reaction of bisphenol-A on contact with epichlorohydrin in the presence of a basic catalyst. This variety of epoxy resin has the lowest molecular weight.
Aliphatic Epoxy Resins
These types of epoxy resins are produced either as a result of double bond epoxidation (involving cycloaliphatic epoxides and epoxidized vegetable oils) or reaction with epichlorohydrin (glycidyl ethers and esters). Cycloaliphatic epoxides feature one or more aliphatic ring in the molecule containing the oxirane ring. They have a defined aliphatic structure, high oxirane content, and absence of chlorine. This makes for low levels of viscosity, good weather resistance, low dielectric constants, and high Tg.
Novolac Epoxy Resins
These types of resins are produced as a result of contact and reaction between phenol and methanol (formaldehyde). The reaction of epichlorohydrin and novolacs results in the formation of novolacs with glycidl residues including epoxyphenol novolac (EPN) or epoxycresol novolac (ECN). Such epoxies do not contain solvents or volatile organic compounds. Being free of VOCs, they are extremely safe to use and respirators aren’t required. They have a relatively high level of adhesive strength, making for good levels of coverage. Protection and durability are also assured in the application of these resins.
Halogenated Epoxy Resins
These epoxy resins are admixed for special properties. This involves the application and mixture of brominated and fluorinated varieties. Brominated bisphenol A is the preferred option for flame resistance and electrical applications. However, the commercial production and use of such resins is limited due to the associated cost and low Tg.
Epoxy Resin Diluents
The creation of epoxy diluents involves the glycidylation of aliphatic alcohols or polyols. The materials produced as a result of such processes may be either monofunctional (e.g. dodecanol glycidyl ether), difunctional (butanediol diglycidyl ether), or higher functionality (e.g. trimethylolpropane triglycidyl ether).
Glycidylamine Epoxy Resins
These epoxy resins have relatively high levels of functionality and are formed as a result of the contact reaction between aromatic amines and epichlorohydrin. Industrial grades include triglycidyl-p-aminophenol (functionality 3) and N,N,N′,N′-tetraglycidyl-bis-(4-aminophenyl)-methane (functionality 4). They have a low-medium viscosity at room temperature, making them easier to process than EPN or ECN varieties.
Epoxy Putty

Epoxy putty may refer to any one of a collection of room-temperature hardening substances, used as space-filling adhesives. The compositions of such putty may vary, depending on the manufacturer and application. They perform the function of strong adhesive fills, which bind, set, and waterproof a variety of materials. The waterproof sealing is assured upon the application of epoxy putty.
Curing Time and Process for Epoxy Resin
Uncured epoxy resins typically have poor mechanical, chemical, and heat resistance properties. However, you can transform such properties through curing, involving the reaction of resin with suitable curatives for the formation of cross-linked thermoset structures. There is some variation in the curing times required for different epoxy pastes and putties. It’s generally recommended that you cure the epoxy warm, slow, and long if the project is important. You should allow up to 72 hours for the setup of epoxy and the formation of strong adhesive bonds. The full curing time should always be allowed for jobs that require the application of high pressure or stress.
The curing of epoxy resin may either involve reaction with itself (homopolymerisation) or the formation of a copopolymer featuring polyfunctional curatives or hardeners. Varieties of epoxy resin hardeners include amines, acids, acid anhydrides, phenols, alcohols and thiols. The respective levels of reactivity are phenol < anhydride < aromatic amine < cycloaliphatic amine < aliphatic amine < thiol. You may increase the speed of the curing reaction through the addition of small quantities of accelerators such as tertiary amines, carboxylic acids and alcohols.
Epoxy Resin Uses and Application Methods
There is a wide variety of uses for epoxy resin, including coating, adhesion, and the formation of composite materials including those using carbon fibre and fibreglass reinforcements. It is possible to alter the properties of epoxies such as silver-filled epoxies featuring high levels of electrical conductivity.
Consider the uses of the epoxy resin varieties highlighted in this content:
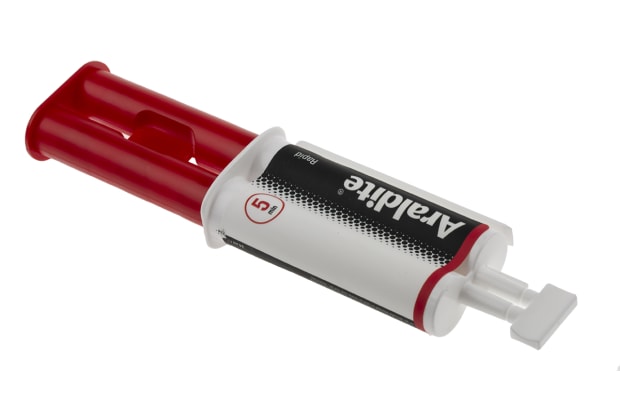

Araldite Rapid Epoxy Adhesive
Material Compatibility :
- Ceramics, wood, chipboard, glass, metal, most hard plastics
Epoxy Colour :
- Clear
Araldite Fusion Epoxy Adhesive
Material Compatibility :
- Ceramics, wood, glass, metal, hard plastics, stone, marble, leather, porcelain, brick, concrete
Epoxy Colour :
- Transparent

Scotch-Weld Epoxy Adhesive
Material Compatibility :
- Plastics, composites, metal
Epoxy Colour :
- Various

Loctite Hysol Epoxy Adhesive
Material Compatibility :
- Ceramics, metal, plastics
Epoxy Colour :
- Various
Epoxy Resin Adhesives
Epoxy adhesives fall under the category of structural adhesives or engineering adhesives, with chemical varieties including polyurethane, acrylic, and cyanoacrylate. Such adhesives may be used for the effective binding of aircraft parts, golf clubs, skis, and snowboards. They also allow for the strong adhesion of wood, metal, glass, stone and other materials. However, the adhesion won’t be as strong at temperatures in excess of 350°F (177°C).
Epoxy Resin Uses for Industrial Tools
Epoxy resin can be used for the strong binding and production of tools such as moulds, master models, laminates, castings, and fixtures. Such plastic tooling is the ideal replacement for materials such as metal and wood. It allows for the achievement of greater efficiency and reduction in the expense and lead times for a range of industrial processes.
Epoxy Resin for Electrical Applications
Epoxy resin is commonly used by workers in the electrical industry for application in the building of motors, generators, transformers, insulators, and printed wiring boards (PWBs). The resins have high levels of electrical insulation and ensure the protection of components from short-circuiting due to the accumulation of dust and moisture.
Epoxy Resin for Consumers
The high levels of adhesion mean that epoxy resin is a popular consumer choice for the repair and maintenance of domestic objects. It allows for the relatively rapid and effective fixing of fragile items such as glass, ceramic, and china. It can also be used for the repair of domestic items made from materials such as wood, metal, and latex.
Epoxy Resin for Artwork and DIY
Epoxy resin can be combined with pigment for a variety of artistic applications. Layers may be added in the creation of a complete picture. Other common uses include the decoration of jewellery and decoupage of work surfaces.
Epoxy Coatings and Painting
Epoxy paint, otherwise known as epoxy floor coating, is commonly used for the coverage of garages, basements, and patio floors. Straight epoxy paint will feature a mixture of acrylic paint and epoxy of the one-part variety. Variations in colouring can be achieved through the application of acrylic epoxy paint, which dries in the same way as regular paint. This paint can be purchased in colours such as metallic blue and cream for an attractive finish.
The epoxy coating is made out of a compound, featuring the distinct elements of epoxy resin and polyamine hardener. The mixing of these elements results in a chemical reaction involving cross-linking during the curing process. Epoxy coatings provide a high level of protection against abrasion, turbulence, corrosive fluids, and extreme temperatures.

Benefits of Epoxy Coating:
- Durability
- Non-toxicity
- Weather resistance
- Impact resistance
- Chemical resistance
- Cleanliness and ease of maintenance
FAQs
How Do You Remove Epoxy Resin?
Epoxy resin isn’t the easiest substance to remove, due to its high adhesive properties. However, the process will be far easier if the resin hasn’t set. In this instance, you can use white vinegar or methylated spirit for removal with a cloth.
The following methods may be used for the removal of hardened epoxy resin:
- Sanding or scraping – such methods may be sufficient if only a small amount of the resin has set
- Using acetone – acetone can be used for the effective removal of epoxy resin from wood or concrete surfaces. However, you should ensure a good level of ventilation and keep the acetone away from flammable items
- Using a heat gun – a heat gun can be used for the effective softening and removal of epoxy resin. A plastic scraper can then be used for removal of the epoxy. You should wear thick work gloves, goggles, and a mask for personal safety
- Using chemicals – epoxy which has set on plastic or glass may be effectively removed with chemicals. They will soften the epoxy in preparation for removal with a scraper. The application of paint thinner may allow for the removal of particularly stubborn epoxy
How Do You Colour Epoxy Resin or is it Pre-Mixed?
It is possible to buy epoxy resin in a wide range of colours and shades but you can also add certain materials to colour epoxy resin yourself. Each material has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
The process of colouring epoxy resin should begin with the combination of equal parts epoxy resin and hardener within a mixing cup. The solution should then be gently stirred until the bubbles are removed. The next step will be to add your selected colourant in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. One gram of powdered colourant should be added for each ounce of epoxy resin liquid. The colourant should then be mixed until it becomes opaque. The combined solution may then be applied to the material.
How Strong is Epoxy Resin?
You should be aware that there is some variation in the strength of epoxy resin varieties. The key strength values include shear strength, compressive strength, flexural strength, and peel strength. Epoxy adhesives offer the greatest level of tensile strength, with single component heat-curable adhesives typically having a strength of 35-41 N/mm2 (5100-6000 psi).
Is There Anything That Epoxy Resin Won’t Stick to?
The types of surfaces which epoxy resin won’t stick to include:
- Wax
- Polyethylene plastics
- Silicone
- Greasy surfaces
- Masking tape
How Do You Polish Epoxy Resin-Covered Surfaces?
Surfaces that are finished with epoxy resin but have taken on a dull or scratched appearance may be polished for optimum appearance. This will involve the basic steps of cleaning, sanding, and applying a polishing compound. You should then proceed to the cleaning and sanding of the surface with soap and clean water. Sandpaper may be used for the removal of scratches. You can also remove grit or dust with a towel.
The polishing process should continue with the application of the polishing compound across the resin surface. Such a compound should be applied to a small area initially with a microfibre cloth. You may then use a buffing wheel or polishing tool for more general application. The finished resin surface should have a smooth and shiny appearance.
How Do You Use Epoxy Resin on Wood?
You should begin the application process by ensuring that the wooden surface is clean and dry. It might be necessary to sand non-porous surfaces. An orbital sander may be used to prevent stress marks in the preparation of wood with a large surface area. You should then proceed to cover the porous surfaces with mixed and unthickened epoxy. It is advisable to pour the epoxy gradually for the prevention of air bubbles. However, a pin or other sharp object may be used for the removal of any bubbles which do appear. The final step will be to cover the resin and allow sufficient time for it to cure fully.



