- Automation & Control Gear
- Cables & Wires
- Enclosures & Server Racks
- Fuses & Circuit Breakers
- HVAC, Fans & Thermal Management
- Lighting
- Relays & Signal Conditioning
- Switches
- Batteries & Chargers
- Connectors
- Displays & Optoelectronics
- ESD Control, Cleanroom & PCB Prototyping
- Passive Components
- Power Supplies & Transformers
- Raspberry Pi, Arduino, ROCK, STEM Education & Development Tools
- Semiconductors
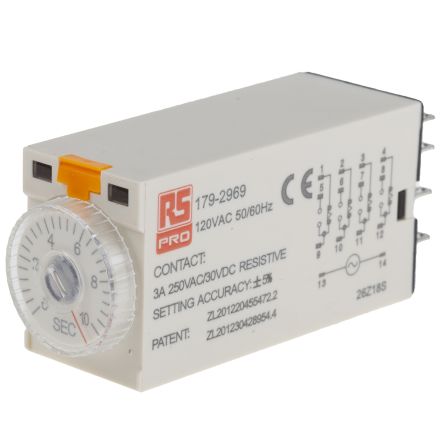
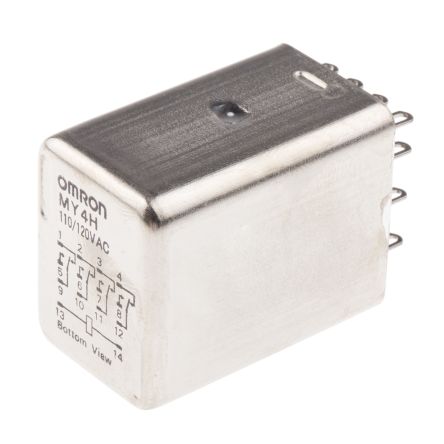
Relays
Relays are essential electromagnetic switches that operate using a relatively small current to control larger currents. Their unique design enables them to switch or amplify substantial electrical loads, making them vital components in various applications. Since their inception in the 19th century, relays have evolved from being primarily used in the telecommunications industry to becoming integral in sectors such as industrial automation, automotive systems, computing, and medical research. Today, relay switches play a crucial role in everyday devices, enhancing functionality and safety.
How Does a General Purpose Relay Work?
A general purpose electrical relay switch operates based on electromagnetic principles. At its core, the relay consists of a coil of wire (typically copper for its low resistance and efficiency in power transmission), which transforms into a magnet when it receives an electric current.
Relays function as a bridge between devices, receiving an input signal from one device and transmitting an output signal to another. The electromagnetic current generated by the electrical input activates the relay, causing its contacts to open or close, thus determining the transmission or the blockage of the electrical signal to the subsequent device. This mechanism is pivotal in many applications, from simple circuit control to complex automated systems.
What Are General Purpose Relays Used For?
Relay switches serve a multitude of functions across various applications due to their versatility and reliability:
- Control High-Power Circuits: Electric relays allow low-power control circuits to manage high-power loads safely. This isolation protects sensitive components from potentially damaging voltages and currents.
- Signal Amplification: In scenarios where control signals are weak, relays can amplify these signals to effectively control larger devices.
- Automated Control Systems: Relay switches are integral in automation systems, working alongside Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and sensors to facilitate seamless operations in industrial processes.
- Safety Applications: Many electric relays are designed with safety features that ensure critical functions operate correctly, minimizing risks in industrial environments.
- Timing Functions: Timer relays can manage delays or periodic operations in various applications, such as lighting controls and machinery operation.
Different Types of Relays Available
Relays come in various types, each designed for specific applications and operational requirements. Here’s an overview of some common types of relays:
- Electromechanical Relays (EMR): Electromechanical relays utilise an electromagnetic coil to mechanically operate a switch. Known for their reliability and versatility, they can control high-power circuits effectively. However, EMRs may experience wear over time due to their moving parts, which can affect longevity in high-frequency applications.
- Latching Relays: Latching relays are operated by a magnetic or mechanical system that retains their position even when the power is turned off. This feature makes them ideal for applications where power conservation is essential, such as automatic doors, gates, and certain lighting systems. Latching relays can be reset by applying a specific signal, allowing for efficient control without continuous power consumption.
- Non-Latching Relays: These relays return to their initial position once power is removed from the circuit. They are typically used in push-button applications, such as keyboards and switches, where momentary operation is required. These relays are straightforward and effective for controlling devices that do not require a maintained state.
- Reed Relays: Reed relays consist of two magnetic reeds sealed within a glass tube filled with inert gas. When energised, the reeds come together to complete a circuit. Reed relays are ideal for low-power applications and are frequently used in telecommunications and security systems due to their fast switching capabilities and high isolation. However, they typically have lower current handling compared to other relay types.
- Solid-State Relays (SSR): Solid-state relays use semiconductor devices instead of mechanical components to switch circuits. They offer faster switching speeds, longer operational life, and resistance to shock and vibration, making them ideal for applications requiring high reliability, such as heating systems and motor control. SSRs also have no moving parts, which contributes to their longer operational life compared to electromechanical relays.
- High Frequency Electromagnetic Relays: Suitable for high voltage environments, these relays are frequently used in radio systems and testing equipment where standard relays may not perform efficiently due to frequency limitations.
- RF Relays: RF (Radio Frequency) relays are specifically designed to manage radio frequency signals, they are essential in communication systems for separating the circuits responsible for receiving and transmitting signals.
- Power Relays: These relays are used to control larger electrical loads and are critical in automation processes. They can handle higher current ratings than standard relays, making them essential for industrial applications where robust performance is required.
- Safety Relays: Designed for safety applications, these ensure that critical functions operate correctly to prevent hazards in industrial environments. These relays often include features such as redundancy and self-monitoring capabilities to enhance safety.
- Timer Relays: Timer relays introduce delays or timing functions into electrical circuits, allowing devices to operate on a schedule or after a specified period. They are widely used in lighting controls, machinery operations, and other applications where timing is critical.
At RS, we offer a broad range of relay switches from the most trusted electrical relay suppliers worldwide.
Industrial Applications of Relay Switches
Relay switches are used in various industries, with specific types tailored to meet distinct requirements:
- Discrete Manufacturing: Utilises electromagnetic relays for controlling assembly line processes and machinery operations.
- Process Manufacturing: Employs electrical relay switches to manage and automate production processes, ensuring efficiency and machine safety.
- Energy & Utilities: Uses power relays to monitor and control electrical distribution systems, enhancing operational safety and reliability.
- Facilities & Intralogistics: Utilises latching relays for automated systems, ensuring seamless control of lighting and access systems.
Delivery Information
As a trusted supplier of electrical components in Singapore, RS provides an extensive range of electric relays, featuring top manufacturers like Omron, TE Connectivity, and RS PRO. We offer fast delivery options, including next-working-day delivery for most online orders within Singapore (Terms & Conditions apply). For more details on our delivery services and applicable fees, please visit our Delivery page.
Guides & Articles