- Automation & Control Gear
- Cables & Wires
- Enclosures & Server Racks
- Fuses & Circuit Breakers
- HVAC, Fans & Thermal Management
- Lighting
- Relays & Signal Conditioning
- Switches
- Batteries & Chargers
- Connectors
- Displays & Optoelectronics
- ESD Control, Cleanroom & PCB Prototyping
- Passive Components
- Power Supplies & Transformers
- Raspberry Pi, Arduino, ROCK, STEM Education & Development Tools
- Semiconductors
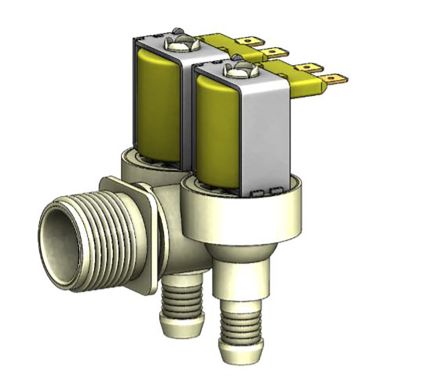
Solenoid Valves
A solenoid valve is an electromechanical device used to control the flow of fluids, such as water, gas, or oil, through a pipeline. It is a type of valve that uses an electric current to open or close the valve mechanism. You can learn more in our comprehensive guide here.
The solenoid valve consists of a coil, a plunger, and a valve seat. The coil is an electrical component that generates a magnetic field when an electric current is passed through it. The plunger is a movable component within the coil that is attracted or repelled by the magnetic field. The valve seat is the opening through which the fluid flows and is blocked or allowed based on the position of the plunger.
When the solenoid valve is energized by applying an electric current, the coil creates a magnetic field that pulls the plunger towards the valve seat, allowing the fluid to flow through the valve. When the electric current is turned off, the magnetic field dissipates, and a spring or other mechanism pushes the plunger back, closing the valve and stopping the flow of fluid.
Applications for Solenoid Valves
- Water Control: Solenoid valves are extensively used in plumbing systems to control the flow of water. They are employed in faucets, showers, toilets, and other fixtures to enable automatic on/off control and water conservation. Solenoid valves allow for touchless operation in public restrooms, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
- Irrigation Systems: Solenoid valves play a crucial role in automated irrigation systems. They control the flow of water to different zones in a garden or landscape, allowing for scheduled watering and efficient water distribution. Solenoid valves can be programmed to open and close at specific times or based on sensor inputs, ensuring proper irrigation management.
- Water Filtration and Treatment: Solenoid valves are used in water filtration and treatment systems to regulate the flow of water through different stages of the process. They control the opening and closing of valves to direct water through various filters, softeners, or disinfection units, ensuring effective water purification.
- Water Heater Systems: Solenoid valves are employed in water heater systems to control the flow of hot water. They regulate the inlet and outlet of hot water, ensuring proper temperature control and preventing overflows or scalding incidents.
- Water Softeners: Solenoid valves are integrated into water softening systems to control the flow of water during regeneration cycles. They allow for the precise timing and control of brine solution flow, facilitating the regeneration process for the water softener.
- Dishwashers and Washing Machines: Solenoid valves are found in dishwashers and washing machines to control the water supply. They open and close to allow water to enter the appliance during the appropriate cycle, regulating the water level and ensuring efficient operation.
- Reverse Osmosis Systems: Solenoid valves are utilized in reverse osmosis systems, which are commonly used for water purification. They control the flow of water through the membranes, ensuring the proper functioning of the filtration process.
- Emergency Shut-off Systems: Solenoid valves are incorporated into plumbing systems as emergency shut-off valves. In case of a leak or other emergency, these valves can be remotely or automatically closed to stop the flow of water and minimize damage.