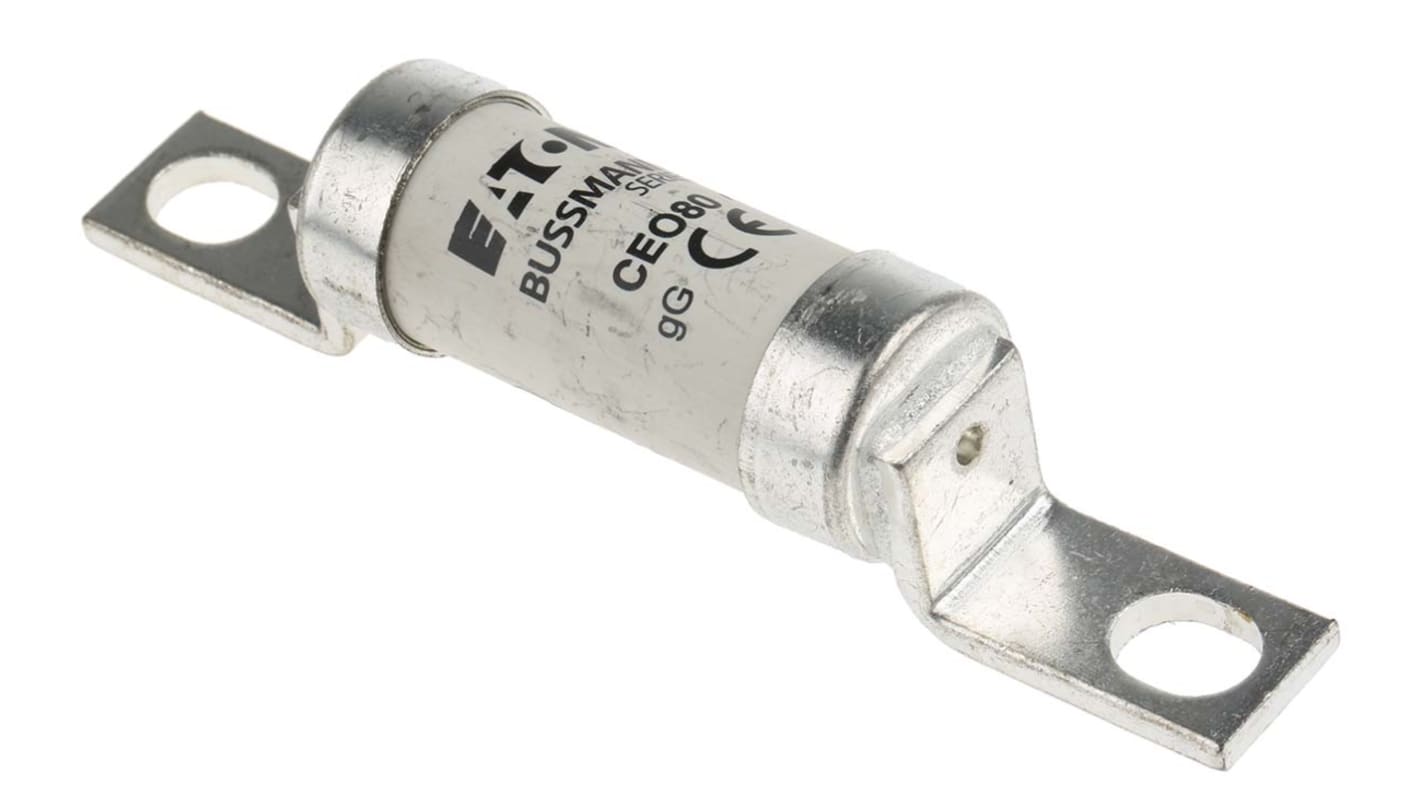
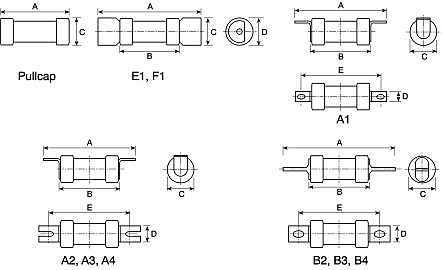
Eaton 80A British Standard Fuse, A4, 500V ac, 94mm
- RS Stock No.:
- 413-535
- Mfr. Part No.:
- CEO80
- Manufacturer:
- Eaton
Bulk discount available
Subtotal (1 unit)**
SGD29.87
(exc. GST)
SGD32.56
(inc. GST)
128 In stock for delivery within 4 working days*
* Delivery dates may change based on your chosen quantity and delivery address.
FREE delivery for orders over SGD150.00 (ex GST)
Real time qty checker
Units | Per unit |
|---|---|
| 1 - 24 | SGD29.87 |
| 25 - 99 | SGD29.76 |
| 100 - 299 | SGD29.31 |
| 300 - 899 | SGD27.98 |
| 900 + | SGD24.18 |
**price indicative
Related links
- Eaton 63A British Standard Fuse 500V ac, 94mm
- Eaton 100A British Standard Fuse 500V ac, 94mm
- Eaton 80A British Standard Fuse 660V ac, 93.7mm
- Eaton 32A Bolted Tag Fuse 500V ac, 94mm
- Eaton 32A British Standard Fuse 500V, 94mm
- Eaton 50A British Standard Fuse 500V, 94mm
- Eaton 40A British Standard Fuse 500V, 94mm
- RS PRO 80A British Standard Fuse 550V ac, 94mm