- Automation & Control Gear
- Cables & Wires
- Enclosures & Server Racks
- Fuses & Circuit Breakers
- HVAC, Fans & Thermal Management
- Lighting
- Relays & Signal Conditioning
- Switches
- Batteries & Chargers
- Connectors
- Displays & Optoelectronics
- ESD Control, Cleanroom & PCB Prototyping
- Passive Components
- Power Supplies & Transformers
- Raspberry Pi, Arduino, ROCK, STEM Education & Development Tools
- Semiconductors
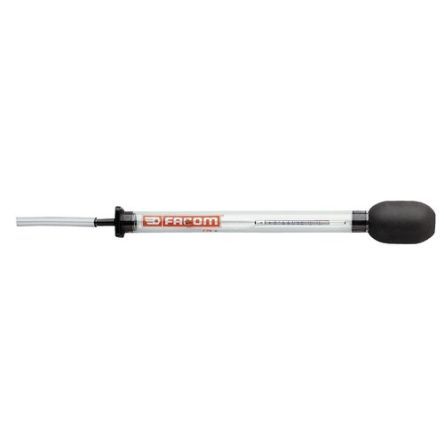
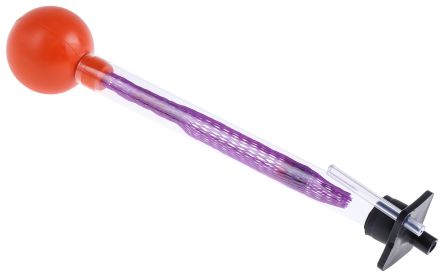
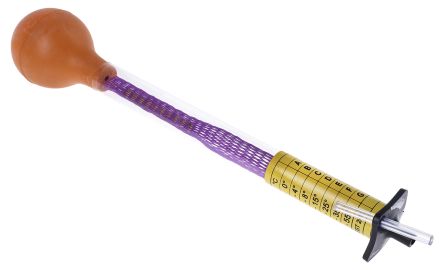
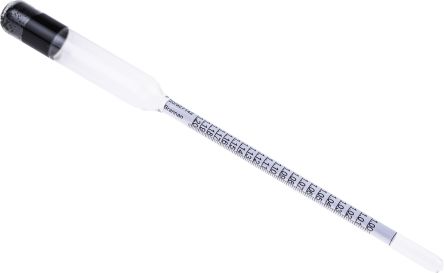
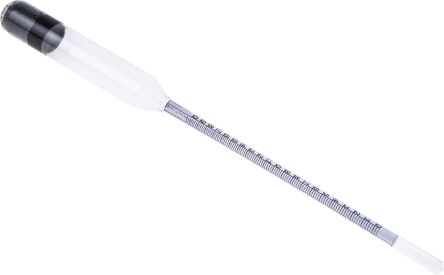
Hydrometers
A hydrometer is an instrument that measures the specific gravity or relative density of a liquid in relation to water. They are typically constructed of a glass cylinder (similar to laboratory cylinders), complete with a weighted bulb that floats in liquid. Hydrometers are divided into two categories, those liquids that are heavier than water and those that are lighter than water.
How Hydrometers work
To operate the hydrometer, you place it in the liquid and take a reading from where the hydrometer breaches the surface. This reading will give you the specific gravity of the water. In high density liquids the hydrometer will float much higher than in low density liquids. Hydrometers can also be used to measure the temperature at a specific range depending upon your specific requirements.
Specialised variants are available depending on their application. For example, a lactometer is used to check the purity of dairy products, whereas an alcoholmeter indicates the alcoholic strength of a liquid (where water and alcohol have been mixed) and a brix hydrometer is used to measure the percentage of sugar and is often used within wine production.
Features and Benefits of Hydrometers:
- Accurate Density Measurement - hydrometers measure the density of liquids with precise and reliable results
- Easy-to-Use - straightforward design allows for simple operation to quickly obtain density readings without the need for complex calibration or setup
- Versatility – can accommodate a wide range of liquid types, such as oils, solvents, acids, and more. Their adaptability makes them indispensable in fields like brewing, chemical analysis, pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and automotive industries.
- Cost-Effective – they are an affordable solution for density measurement compared to more sophisticated instruments
Applications of Hydrometers:
Hydrometers are essential tools that enable accurate density measurements across a multitude of industries and scientific applications including:
- Brewing and Beverage Industry
- Chemical Analysis
- Automotive and Battery Maintenance
- Industrial Processes such as petrochemical, pharmaceutical, and food